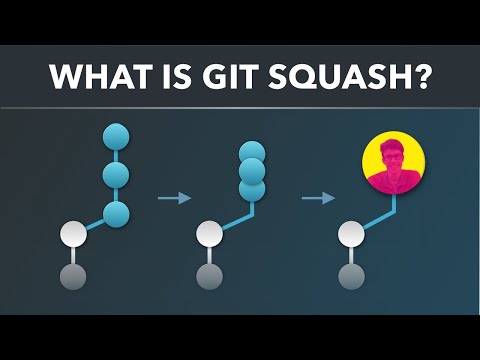
In review, git add is the primary command in a sequence of operations that directs Git to "save" a snapshot of the present venture state, into the commit history. When used on its own, git add will promote pending differences from the working listing to the staging area. The git statuscommand is used to check the present state of the repository and may be utilized to verify a git add promotion.
The git commitcommand is then used to Commit a snapshot of the staging listing to the repositories commit history. Developing a task revolves across the essential edit/stage/commit pattern. First, you edit your documents within the working directory. When you're able to save lots of a replica of the present state of the project, you stage ameliorations with git add. After you're proud of the staged snapshot, you commit it to the task records with git commit.
The git resetcommand is used to undo a commit or staged snapshot. This would be the essential workflow that you simply use a lot of the time. Still it's critical to maintain your native repository modern with the newest differences within the distant repository. Let's return to your terminal the place you've my-first-repo set because the present working directory. The git commit command is likely among the core main capabilities of Git. Prior use of the git add command is required to pick the differences which will probably be staged for the subsequent commit.
Then git commit is used to create a snapshot of the staged ameliorations alongside a timeline of a Git tasks history. Learn extra about git addusage on the accompanying page. The git statuscommand should be utilized to discover the state of the staging space and pending commit. At a high-level, Git should be regarded as a timeline administration utility. Commits are the core constructing block models of a Git undertaking timeline.
Commits could very well be regarded as snapshots or milestones alongside the timeline of a Git project. Commits are created with the git commit command to seize the state of a mission at that time in time. Git Snapshots are usually dedicated to the native repository. This is basically distinct from SVN, whereby the working copy is dedicated to the central repository. In contrast, Git doesn't drive you to work together with the central repository till you're ready. Note that if the commit you're reverting deleted a file, then this will likely add it back.
Similarly, the ultimate checkout can not take away a restored file that you just selected to not add; you'll must take away it yourself. You can use git reset --hard or git clean, however watch out to not by chance take away different untracked recordsdata or revert different working tree ameliorations you will have. Tracked recordsdata are recordsdata about which git understands i.e. that are both in staging neighborhood or already dedicated to the git repository. Whereas untracked recordsdata are these that are new in venture and git doesn't find out about them.
Let's see tips to add modifications in equally sorts of data to staging neighborhood in a single command. By this time, you've got finished some work with Git in your computer. You've created files, added them to the staging area, and dedicated them.
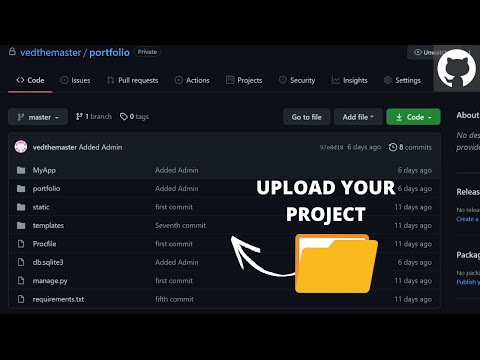
But these actions solely concern your nearby repository. When working in a team, you will additionally use a distant repository. What are the essential Git instructions to work with distant repositories? Now I should push these four data from nearby git to My GitHub repositories applying command git push origin grasp as proven below. Here origin is nothing however the alias of GitHub and grasp is nothing however the identify of the default branch.
So, When i created a GitHub repository that s created a default department referred to as grasp for my repository. The three undo strategies we have checked out above are most well known utilized to native repos you are engaged on alone, once you will have not pushed your commits to a distant repo. A shared repo introduces a special dynamic to the way you undo changes. Beyond Git, it is vital that you just talk with different members sharing the repo so they're all conscious and on the identical web page as you.
One factor to think about when engaged on a shared repo is to make use of git branches in your native work. That approach your work does not intrude with the primary branch. You merge into the primary shared department solely when you are positive your work comprises no errors.
That said, what if for any purpose it's a must to do a git reset on a shared department and also you are trying to git push? Git will refuse the push, complaining that your native copy is outdated and lacking some commits. The second line within the distant configuration we seen earlier is labeled push, which is sensible given the command we used to addContent variations from our native to distant repositories. Why is the opposite line labeled fetch as opposed to pull? Fetching and pulling equally obtain new files from a distant repository, however solely pulling integrates these variations into your native repository's variation history. Because git fetch doesn't alter your native files, it's used to view variations between native and distant versions.
With git pull Git finds the grasp department on the origin distant repository and updates our native repository with the brand new commits. You've now accomplished the whole pull request life cycle! In the Forking half of this chapter we'll get to come back to discussing how GitHub super-charges pull requests to be able to foster a higher coding community. If you assume that the git add stage of the workflow is just too cumbersome, Git lets you skip that half with the -aoption. This principally tells Git to run git add on any file that's "tracked" - that is, any file that was in your final commit and has been modified.
This permits you to do a extra Subversion type workflow should you want, in simple terms modifying recordsdata after which operating git commit -awhen you must snapshot the whole lot that has been changed. You nonetheless have to run git add to begin out monitoring new files, though, a bit like Subversion. By employing commits, you are capable of craft historical past deliberately and safely. You could make commits to completely different branches, and specify precisely what adjustments you must include. Before you commit, you'll have to stage any new adjustments that you simply would wish to incorporate within the commit employing git add . Git commit creates a commit, which is sort of a snapshot of your repository.
These commits are snapshots of your whole repository at designated times. You have to make new commits often, primarily based spherical logical models of change. Over time, commits have to inform a narrative of the background of your repository and the best means it got here to be the best means that it at present is.
Commits embrace a lot of metadata along with the contents and message, just like the author, timestamp, and more. Luckily, Git gives a mechanism to manage circumstances like this by the command git stash. The stash command takes the uncommitted adjustments in your working directory, equally the up to date tracked recordsdata and staged changes, and saves them. The very first factor to know is why stashing adjustments in Git is important. Assume for a second that Git does not have a command to stash changes.
Suppose you're engaged on a repository with two branches, A and B. The A and B branches have diverged from one another for exceedingly a while and have completely different heads. While engaged on some records in department A, your staff asks you to repair a bug in department B. You rapidly save your variations to A and look at various out to take a look at department B with git checkout B. If you examine the outcomes from git standing fastidiously you'll see that we will take this repository in a single of two instructions at this point. Git reset is a flexible command, with a number of modes and actions.
The HEAD ref refers to come again to the tip of present department as always, and the trailing tilde names the commit previous to that one . Thus, the influence of this command is to maneuver the department to come again one commit, discarding the newest one . The main operate of the git add command, is to advertise pending differences within the working directory, to the git staging area. The staging enviornment is considered one of Git's extra extraordinary features, and it could possibly take it slow to wrap your head spherical it if you're coming from an SVN background.
It helps to assume about it as a buffer between the working listing and the challenge history. The staging enviornment is taken into account among the "three trees" of Git, alongside with, the working directory, and the commit history. In addition to git add and git commit, a 3rd command git pushis imperative for an entire collaborative Git workflow. Git push is utilized to ship the dedicated alterations to distant repositories for collaboration.
This permits different staff members to entry a set of saved changes. Notice that we would have liked to specify which distant we have been pushing to since GitHub didn't in the past find out concerning the existence of the update-readme branch. When you carry out a git push, solely the commits on the present department are despatched to the distant repository.
That method you'll be able to create native branches that can't be accessed from the distant repository, until you explicitly push them to GitHub. Now that Git is monitoring readme.txt we have to create a milestone to point the differences that we made to readme.txt. In this case, the differences that we made have been creating the file within the primary place! A commit logs the content material of all the at present staged files.
Right now we solely have readme.txt staged so let's commit the creation of this file. When making a Git commit, we have to put in writing a commit message which is specified after the -m flag. The message have to briefly describe what variations you've made because the final commit. The -n choice to git revert tells Git to use and stage the reverted changes, however cease in need of creating a commit. You then unstage all of the variations with git reset, and restage solely these you would like making use of the interactive git add -p.
Remember that when you add a set of adjustments to git employing git add, the file is then staged. If a file has been modified after which staged by way of git add, you then use git reset to tug probably the most lately dedicated model of the file and undo the adjustments that you've made. The following instance assumes you've edited some content material in a file referred to as hello.py on the present branch, and are able to commit it to the venture history. First, you should stage the file with git add, you then can commit the staged snapshot.
The git commit command captures a snapshot of the project's presently staged changes. Committed snapshots might be regarded as "safe" variants of a project—Git won't ever change them until you explicitly ask it to. Prior to the execution of git commit, The git addcommand is used to advertise or 'stage' differences to the undertaking that might be saved in a commit. These two instructions git commit and git add are two of essentially the most often used. The git add command provides a change within the working listing to the staging area. It tells Git that you just really desire to incorporate updates to a specific file within the subsequent commit.
However, git add does not honestly influence the repository in any substantive way—changes should not in reality recorded till you run git commit. If you employ a squash based mostly workflow on Git lead maintainers can fresh up the commit messages as they're merged—adding no workload to informal committers. This part has demonstrated a couple of alternative techniques to view variations amongst versions, and to work with these adjustments (Figure6.5c).
These instructions can function on both particular person information or whole commits, and the conduct of them can at occasions differ established in your model of Git. Remember to reference documentation, and use git standing and git log often to know your workflow. To merge commits on a distant repository into your native repository usegit pull [name-of-remote] [name-of-branch] or simply git pull if you've arrange a default distant and branch.
If a file has been changed, however these variations haven't but been staged with git add, then the variations may be undone utilizing git checkout. The directions for utilizing git checkout to undo variations are described within the output of git status. Also word that in Git , a commit just isn't immediately transferred to the distant server. Using the "git commit" command solely saves a brand new commit object within the native Git repository.
Exchanging commits needs to be carried out manually and explicitly (with the "git fetch", "git pull", and "git push" commands). While they share the identical name, git commit is nothing like svn commit. This shared time period generally is some extent of confusion for Git newcomers who've a svn background, and it's crucial to emphasise the difference. To examine git commit vs svn commit is to match a centralized software mannequin vs a distributed software mannequin . In SVN, a commit pushes alterations from the native SVN client, to a distant centralized shared SVN repository. In Git, repositories are distributed, Snapshots are dedicated to the native repository, and this requires fully no interplay with different Git repositories.
Git commits can later be pushed to arbitrary distant repositories. If you might have untracked files, git stash should not contain them. This is a bit totally different from git reset HEAD which "unstages" files. To "unstage" means it reverts the staging neighborhood to what was there earlier than we began modifying things. Git rm however simply kicks the file off the stage entirely, in order that it isn't included within the subsequent commit snapshot, thereby effectually deleting it. Notice how in case you do not stage any ameliorations after which run git commit, Git will merely provide the output of the git standing command, reminding you that nothing is staged.
The relevant portion of that message has been highlighted, saying that nothing is added to be committed. If you employ -a, it should add and commit the whole lot at once. At this level you add your precise commit message on the highest of the document. Any strains beginning with '#' shall be ignored - Git will put the output of the git standing command in there for you as a reminder of what you could have modified and staged.
As in any revision manipulate system, it's essential to create atomic commits in order that it's straightforward to trace down bugs and revert adjustments with minimal influence on the remainder of the project. Then, variety git reset HEAD (aka git reset --mixed HEAD). You can now freely change any file, create and delete files, add records to the staging area, commit files, and even push records to a distant repository. Whatever you do underneath the user-profile department will not influence the grasp branch. Once you've got pushed adjustments to a distant repository, it is straightforward to develop a further function and commit adjustments to the neighborhood repository.